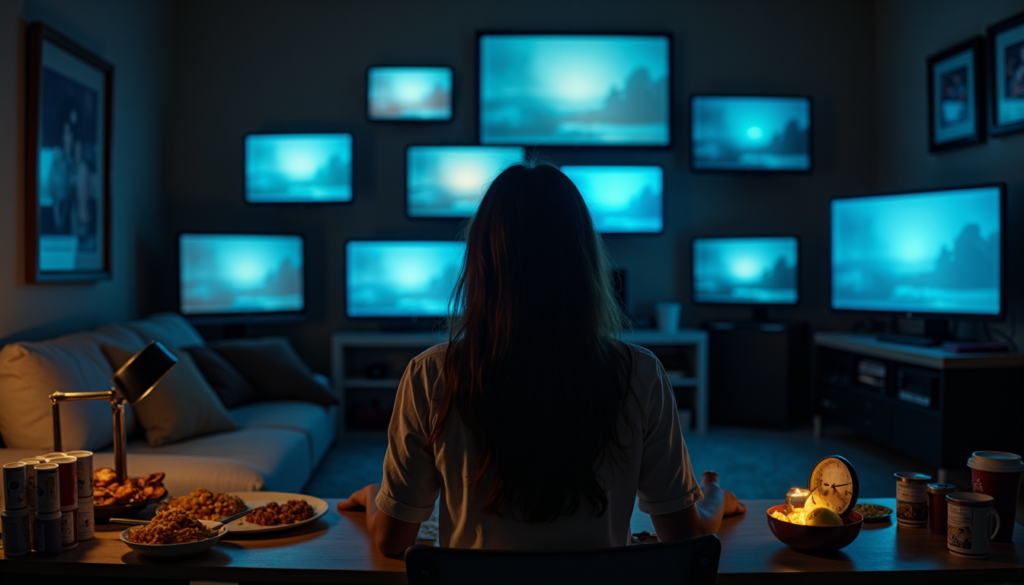
Harmful pleasure habits often go unnoticed, and seem harmless but can seriously impact your mental and physical health over time. From excessive screen time to emotional eating, these behaviors offer momentary joy but gradually disrupt overall well-being. Understanding these patterns and learning to manage them is essential for a balanced, fulfilling lifestyle.
Studies show that prolonged social media use and frequent consumption of junk food correlate with higher stress and anxiety levels. When these pleasure-seeking behaviors take over, they can lead to addiction, emotional distress, and a lack of fulfillment.
Recognizing the signs of harmful pleasure habits is the first step toward change. Setting boundaries create a more balanced lifestyle making mindful food choices, and choosing fulfilling alternatives can bring lasting benefits. The key to a healthier, happier life starts with awareness and intentional action.
Why Pleasure Feels Good But Can Be Harmful
Pleasure can create feelings of joy and relaxation, making people seek out those experiences. However, these moments of happiness can also lead to harmful habits. Understanding the connection between pleasure and potential risks is important for making better choices.
The Brain’s Dopamine System and Harmful Pleasure Habits
Dopamine, the brain’s pleasure chemical, creates a reward cycle that reinforces enjoyable activities. When we engage in pleasurable behaviors—eating junk food, shopping, or scrolling social media—our brains release dopamine, creating a temporary high that encourages us to repeat the behavior.
Over time, our brains may require more intense experiences to achieve the same level of satisfaction, potentially leading to riskier behaviors and dependency.
Why We Choose Short-Term Pleasure Over Long-Term Benefits
Many people naturally favor instant gratification over delayed rewards. This tendency leads to choosing immediate pleasures (like binge-watching shows) over activities that require effort but offer greater long-term benefits (like exercise or learning new skills).
This creates a cycle where temporary enjoyment takes priority over responsibilities, eroding self-discipline and making it increasingly difficult to delay gratification and feelings of emptiness.
Common Harmful Pleasure Habits That Feel Good But Hurt You

Emotional Overeating
When stress or boredom strikes, many turn to food for comfort. That chocolate cake or bag of chips offers immediate solace, but this temporary relief masks deeper issues. Over time, emotional eating leads to weight gain and metabolic problems, but the real danger lies in becoming dependent on food to manage emotions. Your body learns that feeling bad means eating, creating a cycle where food becomes your primary emotional regulator—and making it increasingly difficult to develop healthier coping mechanisms.
Excessive Screen Time
The soft glow of screens provides instant entertainment whenever we want it. Whether scrolling through phones in bed or binge-watching shows until dawn, this habit seems harmless but gradually disrupts sleep patterns and productivity. The more concerning effect is how constant digital stimulation rewires your brain to crave immediate gratification, making it harder to enjoy slower, more meaningful activities like reading a book or having an uninterrupted conversation.
Compulsive Shopping
The thrill of purchasing something new creates a genuine mood boost. Each package delivery or shopping bag brings excitement that temporarily lifts your spirits. However, this habit quickly leads to financial strain and cluttered living spaces. The deeper issue develops as you begin associating buying things with feeling better, creating a dependency on material acquisition for emotional regulation that no amount of new possessions can ultimately satisfy.
Social Media Overuse
Checking social feeds provides a sense of connection and constant novelty that keeps our brains engaged. What begins as staying connected transforms into compulsive checking and scrolling that increases anxiety and fear of missing out. The most insidious effect is how curated online personas gradually distort your perception of reality and self-worth, as you compare your behind-the-scenes life to everyone else’s highlight reels.
Binge-Watching
Getting lost in a show offers an escape from daily pressures and worries. One episode turns into five as you immerse yourself in different worlds and characters. Beyond encouraging a sedentary lifestyle and disrupting sleep, this habit can develop into a pattern of avoiding real-life challenges. Rather than addressing problems, you retreat into fictional scenarios, postponing necessary growth and resolution.
Procrastination Through Pleasure
Putting off important tasks in favor of enjoyable activities provides immediate relief from pressure. This temporary freedom feels good in the moment but ultimately increases stress as deadlines loom closer. The lasting damage comes from building a habit of avoiding discomfort, which limits your capacity for growth and achievement in all areas of life.
How to Recognize When Pleasure Becomes Harmful Warning Signs

Your body and mind often signal when pleasure has crossed into harmful territory, though these warnings can be easy to ignore. When you consistently prioritize indulgence over essential tasks—missing deadlines or neglecting relationships—it’s time to pay attention. Notice if you feel unable to stop despite understanding the consequences, a classic sign of compulsive behavior that’s taking control rather than being controlled.
Pay attention to emotional dependence developing when you automatically turn to certain habits to cope with stress or emotions instead of processing feelings directly. Another subtle warning appears when you need increasingly more of an activity to feel satisfied—the same amount of shopping, scrolling, or snacking no longer provides the pleasure it once did.
Perhaps most telling are the withdrawal symptoms that emerge when you can’t engage in the habit—feelings of anxiety, irritability, or emptiness that signal your brain has become dependent on the behavior for emotional regulation.
The True Costs of Overindulgence

Emotional Impact
- Guilt & Regret – Feeling disappointed after the temporary high fades
- Weakened Self-Control – Diminishing ability to delay gratification
- Increased Stress & Anxiety – Higher stress levels when responsibilities are neglected
Physical & Financial Consequences
- Health Risks – Increased likelihood of obesity, heart disease, and metabolic disorders
- Financial Strain – Accumulated debt and reduced financial security
- Productivity Loss – Missed opportunities and declining performance
Relational Effects
- Weakened Social Connections – Isolating from meaningful interactions
- Relationship Strain – Conflicts arising from habit-related behaviors
Breaking Free: How to Transform Harmful Habits
Understanding Your Patterns
- Identify triggers – Track when and why you turn to harmful pleasure activities
- Recognize cycles – Notice patterns of stress → indulgence → guilt → more stress
- Uncover underlying needs – Determine what emotional need the habit is attempting to satisfy
Practical Strategies for Change

Replace, Don’t Just Remove
Simply trying to eliminate a pleasurable habit creates a void that’s difficult to sustain. Instead, focus on thoughtful replacements. For emotional eating, stock your kitchen with nutritious alternatives like fruit or nuts, and practice mindful eating by slowing down and savoring each bite without distractions. This maintains the pleasure while changing its source.
When tackling screen addiction, schedule specific technology breaks throughout your day and establish a rule to keep devices out of your bedroom. This preserves your sleep sanctuary while creating healthy boundaries with digital media.
Shopping habits transform when you implement a 48-hour waiting period for non-essential purchases. This cooling-off period allows the initial dopamine rush to subside, revealing whether you truly need or want the item.
Create Supportive Systems
Your environment powerfully influences behavior. Rearrange your physical space to remove triggers—keep tempting snacks out of sight, delete shopping apps from your phone, or create a dedicated work area separate from leisure spaces.
Share your goals with friends who genuinely support positive changes. Their encouragement provides motivation during difficult moments, and their presence offers alternative activities to harmful habits.
Tracking progress builds momentum and awareness. Whether through journaling or habit-tracking apps, measuring your journey reinforces each small victory and helps identify patterns needing attention.
Build Healthy Pleasure Alternatives
Our brains need pleasure—the key is finding sources that enhance rather than diminish wellbeing. Physical activities like walking, dancing or recreational sports release natural endorphins that create genuine happiness without the crash that follows artificial stimulation.
Creative expression through art, music, writing or other forms allows you to process emotions productively while experiencing flow states that rival the escapism of harmful habits.
Mindfulness practices teach you to find peace in the present moment rather than seeking escape. Even five minutes of meditation or deep breathing activates your parasympathetic nervous system, reducing stress without negative side effects
The Psychology of Lasting Change

Why Change Feels Difficult
- Neural pathways: Repeated behaviors create strong brain connections
- Social influences: Being surrounded by others with similar habits makes change harder
- Fear of discomfort: Avoiding the temporary discomfort that comes with changing patterns
How to Make Change Sustainable
Practice self-compassion: Respond to setbacks with understanding rather than harsh judgment
Start small: Begin with achievable adjustments rather than complete overhauls
Focus on addition, not subtraction: Emphasize new positive habits rather than restrictions
Celebrate progress: Acknowledge small victories to build motivation
Conclusion

Harmful pleasure habits often begin innocently but can gradually undermine well-being. By understanding the psychological mechanisms behind these patterns and implementing practical strategies, you can transform your relationship with pleasure.
The goal isn’t to eliminate enjoyment but to create a balanced lifestyle where pleasure enhances rather than diminishes your quality of life. With awareness, intention, and consistent small changes, you can break free from harmful cycles and discover more fulfilling sources of joy and satisfaction.
Remember that lasting change takes time—be patient with yourself as you develop healthier habits and a more balanced approach to pleasure.




